Explain Mean filters.
There are four types of mean filters. They are
(i) Arithmetic mean filter
This is the simplest of the mean filters. Let Sxy represent the set of coordinates in a rectangular subimage window of size m X n, centered at point (x, y).The arithmetic mean filtering process computes the average value of the corrupted image g(x, y) in the area defined by Sxy. The value of the restored image f at any point (x, y) is simply the arithmetic mean computed using the pixels in the region defined by Sxy. In other words

This operation can be implemented using a convolution mask in which all coefficients have value 1/mn
(2) Geometric mean filter
An image restored using a geometric mean filter is given by the expression

Here, each restored pixel is given by the product of the pixels in the subimage window, raised to the power 1/mn. A geometric mean filter achieves smoothing comparable to the arithmetic mean filter, but it tends to lose less image detail in the process.
(3) Harmonic mean filter
The harmonic mean filtering operation is given by the expression

The harmonic mean filter works well for salt noise, but fails for pepper noise. It does well also with other types of noise like Gaussian noise.
(4) Contra harmonic mean filter
The contra harmonic mean filtering operation yields a restored image based on the expression
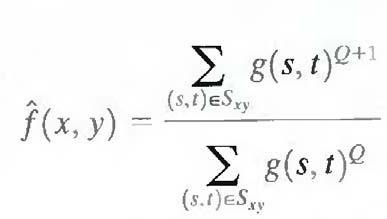
where Q is called the order of the filter. This filter is well suited for reducing or virtually eliminating the effects of salt-and-pepper noise. For positive values of Q, the filter eliminates pepper noise. For negative values of Q it eliminates salt noise. It cannot do both simultaneously. Note that the contra harmonic filter reduces to the arithmetic mean filter if Q = 0, and to the harmonic mean filter if Q = -1.